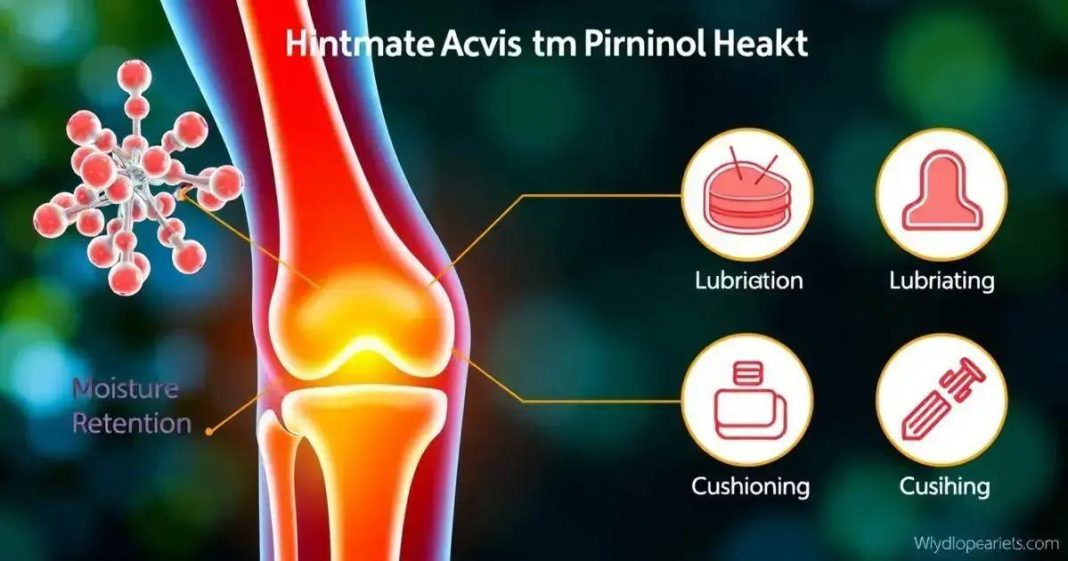
Hyaluronic acid is essential for joint health, providing lubrication and cushioning that can reduce pain, enhance mobility, and support cartilage integrity. Incorporating it through supplements or injections can help manage joint discomfort, but consulting a healthcare provider is recommended before starting any new treatment. Prioritizing hyaluronic acid can lead to improved joint function and overall quality of life.
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the body that plays a crucial role in maintaining joint health. Known for its ability to retain moisture, hyaluronic acid is essential for lubricating joints and providing cushioning to cartilage. This article will explore the benefits of hyaluronic acid for joint health, its applications, and how to incorporate it into your routine.
What is Hyaluronic Acid?
What is Hyaluronic Acid?
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan, a type of molecule found throughout the body, particularly in connective tissues, skin, and synovial fluid. It is renowned for its incredible ability to retain moisture, capable of holding up to 1,000 times its weight in water.
In joints, hyaluronic acid is a key component of synovial fluid, which lubricates and cushions joints, allowing for smooth movement and reducing friction between bones. This substance is also found in cartilage, where it helps maintain its structure and hydration.
As we age, the body’s production of hyaluronic acid decreases, leading to a decline in joint lubrication and an increase in discomfort, stiffness, and pain. This decline can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis and other joint-related issues.
Hyaluronic acid is available in various forms, including dietary supplements, topical creams, and injectable formulations. Its use in joint health has gained popularity due to its potential to alleviate pain and improve mobility in individuals with joint problems.

Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid for Joints
Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid for Joints
Hyaluronic acid offers several significant benefits for joint health, primarily due to its role in maintaining lubrication and cushioning in the joints. Here are some key benefits associated with hyaluronic acid for joints:
- Joint Lubrication: Hyaluronic acid is a vital component of synovial fluid, which lubricates joints and reduces friction between bones. This lubrication is essential for smooth movement and prevents wear and tear on the cartilage.
- Cushioning Effect: By providing cushioning in the joints, hyaluronic acid helps absorb shock during movement, which is particularly beneficial for weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
- Reduces Pain and Discomfort: Studies have shown that hyaluronic acid injections can help alleviate pain in individuals with osteoarthritis by improving joint function and reducing inflammation.
- Enhances Mobility: By improving lubrication and reducing pain, hyaluronic acid can enhance overall joint mobility and flexibility, allowing individuals to engage in physical activities more comfortably.
- Supports Cartilage Health: Hyaluronic acid contributes to the maintenance and regeneration of cartilage, helping to preserve its structure and function. This is crucial for preventing further joint deterioration.
- Promotes Healing: Hyaluronic acid may aid in the healing of damaged joint tissues by providing necessary moisture and support for recovery, especially after injury or surgery.
Incorporating hyaluronic acid into your joint health regimen, whether through supplements or injections, can provide these benefits, making it a valuable option for those experiencing joint pain or discomfort. However, it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
How Hyaluronic Acid Works in the Body
How Hyaluronic Acid Works in the Body
Hyaluronic acid exerts its beneficial effects in the body through several key mechanisms, particularly concerning joint health and function. Here’s how hyaluronic acid works:
- Lubrication of Joints: Hyaluronic acid is a major component of synovial fluid, which serves as a lubricant in joints. It reduces friction between bones during movement, facilitating smoother joint motion and preventing wear and tear on cartilage.
- Cushioning Effect: By providing cushioning, hyaluronic acid helps absorb shock during activities such as walking, running, and jumping. This cushioning effect is especially important for weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
- Support for Cartilage Integrity: Hyaluronic acid plays a role in maintaining the structure of cartilage. It helps retain moisture in the cartilage matrix, which is crucial for cartilage resilience and hydration, preventing degeneration.
- Modulation of Inflammation: Hyaluronic acid has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the joints. By inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, it helps alleviate joint pain and swelling.
- Promotion of Tissue Repair: Hyaluronic acid is involved in the healing processes of damaged tissues. It can enhance the regeneration of cartilage and promote the formation of new blood vessels, aiding in recovery from injuries.
- Hydration of Tissues: As a powerful humectant, hyaluronic acid attracts and retains water, contributing to the hydration of the skin and connective tissues, including those in the joints.
Through these mechanisms, hyaluronic acid works synergistically in the body to support joint health, enhance mobility, and alleviate discomfort. This makes it a valuable component in both dietary supplements and medical treatments for joint-related issues.
Sources of Hyaluronic Acid
Sources of Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid can be obtained from various dietary sources and supplements. Understanding these sources can help individuals ensure they are getting enough hyaluronic acid to support their joint health and overall well-being. Here are some key sources of hyaluronic acid:
- Animal Sources:
- Chicken Combs: The highest concentrations of hyaluronic acid are found in the combs of chickens, which are often used in supplements.
- Bone Broth: Made by simmering animal bones and connective tissues, bone broth contains natural hyaluronic acid and is a nutritious addition to the diet.
- Fish Eyes and Skins: Fish, particularly those with skin, contain hyaluronic acid, contributing to its availability in dietary supplements.
- Plant Sources:
- Root Vegetables: Some root vegetables, such as sweet potatoes and beets, contain small amounts of hyaluronic acid and nutrients that support its production.
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables like spinach and kale may also support the body’s natural production of hyaluronic acid.
- Hyaluronic Acid Supplements:
- Dietary Supplements: Hyaluronic acid is widely available in supplement form, including capsules, tablets, and powders, making it easy to incorporate into your daily routine.
- Injectable Formulations: In medical settings, hyaluronic acid can be injected directly into joints to provide immediate relief from pain and improve mobility.
Incorporating both dietary sources and supplements can help individuals maintain adequate levels of hyaluronic acid, supporting their joint health and overall well-being.
Recommended Dosage and Usage
Recommended Dosage and Usage
When using hyaluronic acid as a supplement for joint health, it’s important to follow appropriate dosage and usage guidelines to ensure safety and effectiveness. Here are some recommendations:
- Typical Dosage: The common dosage for hyaluronic acid supplements ranges from 100 mg to 200 mg per day. However, for individuals seeking treatment for joint pain, higher dosages of up to 1,500 mg per day may be recommended, depending on the specific product and concentration.
- Forms of Hyaluronic Acid: Hyaluronic acid is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, powders, and liquid solutions. Choose the form that is most convenient for you and fits easily into your daily routine.
- Timing of Doses: For optimal absorption and effectiveness, it is recommended to take hyaluronic acid supplements with meals. If using powdered forms, consider mixing it into smoothies, water, or other beverages.
- Duration of Use: Hyaluronic acid can be taken for both short-term and long-term purposes. Many individuals may notice improvements in joint pain and mobility within a few weeks, but continued use may be necessary for sustained benefits.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting hyaluronic acid, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or have underlying health conditions, consult with a healthcare provider. They can help determine the appropriate dosage and ensure that it won’t interact with any medications you may be taking.
By following these dosage and usage recommendations, you can effectively incorporate hyaluronic acid into your health regimen and enjoy its numerous benefits safely.
Conclusion
Hyaluronic acid is a vital substance that plays a crucial role in maintaining joint health and overall well-being.
Its exceptional ability to retain moisture makes it essential for lubricating joints and supporting cartilage integrity.
As collagen and hyaluronic acid levels decline with age, individuals may experience joint discomfort and reduced mobility.
Incorporating hyaluronic acid through dietary supplements or treatments can be an effective strategy for alleviating joint pain and enhancing joint function.
Understanding the importance of hyaluronic acid allows individuals to take proactive steps in managing their joint health.
By prioritizing the use of hyaluronic acid alongside a balanced diet and regular exercise, individuals can promote their joint health, improve their mobility, and enhance their overall quality of life.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Hyaluronic Acid for Joints
What is hyaluronic acid and how does it benefit joints?
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the body that helps lubricate and cushion joints, reducing friction and discomfort during movement.
How does hyaluronic acid improve joint health?
Hyaluronic acid improves joint health by providing lubrication, reducing pain and inflammation, and supporting cartilage health.
What are the common forms of hyaluronic acid supplements?
Hyaluronic acid supplements come in various forms, including capsules, powders, and injectable solutions.
How is hyaluronic acid administered for joint pain?
Hyaluronic acid can be administered through injections directly into the joint space or taken as an oral supplement.
Are there any side effects of using hyaluronic acid for joints?
Hyaluronic acid is generally considered safe, but some individuals may experience mild side effects such as swelling, pain, or irritation at the injection site.
How long does it take to see results from hyaluronic acid injections?
Many individuals may start to notice improvements in joint pain and mobility within a few weeks of receiving hyaluronic acid injections.