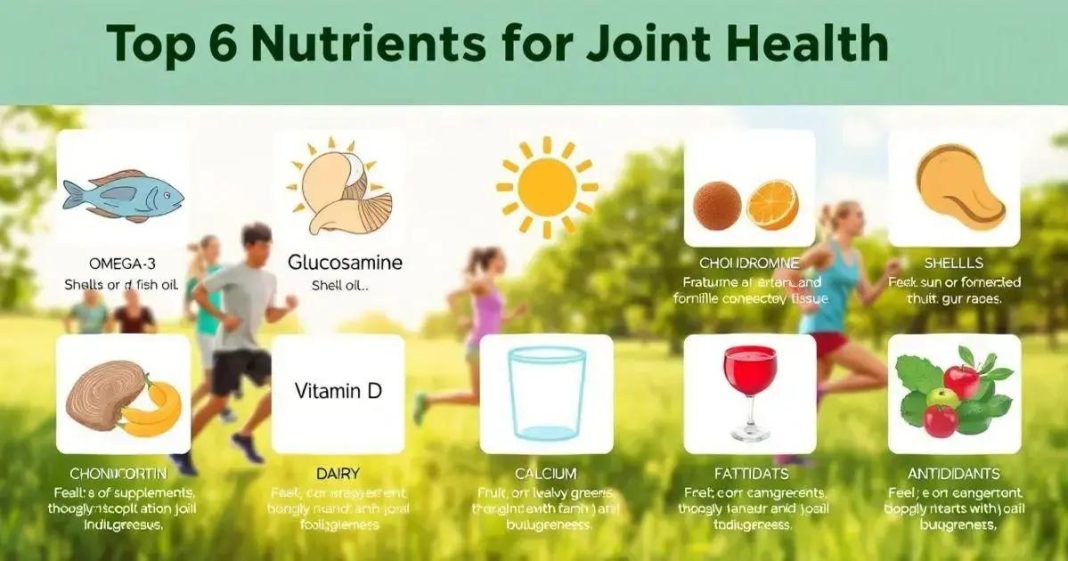
Maintaining joint health is vital for mobility and overall quality of life. Key nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, vitamins C and D, and antioxidants help reduce inflammation and support joint function. A balanced diet rich in whole foods, such as fatty fish and fruits, along with supplements when necessary, can enhance joint health. Regular exercise, adequate rest, and professional guidance are also crucial for optimizing joint function and promoting an active lifestyle.
Nutrients for joints play a critical role in maintaining joint health and preventing discomfort. As we age or engage in physical activities, our joints can become stressed and require additional support. Incorporating the right nutrients into your diet can help improve joint function, reduce inflammation, and enhance mobility. In this article, we’ll explore the top six nutrients for joints and how they contribute to overall joint health.
Understanding Joint Health
Understanding joint health is essential for maintaining mobility and overall well-being. Joints are the connections between bones that allow for movement and flexibility, and they play a critical role in our daily activities. Keeping joints healthy involves recognizing the factors that contribute to their function and the potential risks that can lead to discomfort or injury.
1. Components of Joint Health: Joints are composed of several key structures, including:
- Cartilage: A smooth, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint, providing cushioning and reducing friction during movement.
- Synovial Fluid: A lubricating fluid that fills the joint space, allowing for smooth movement and reducing wear on cartilage.
- Ligaments: Tough bands of tissue that connect bones to each other, providing stability to the joint.
- Tendons: Connective tissues that attach muscles to bones, enabling movement at the joint.
2. Factors Affecting Joint Health: Several factors can influence joint health:
- Age: As we age, cartilage can wear down, and natural collagen production decreases, leading to joint stiffness and pain.
- Activity Level: Regular physical activity helps maintain joint flexibility and strength, while a sedentary lifestyle can lead to stiffness and weakness.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for joint health, helping to reduce inflammation and support tissue repair.
- Weight Management: Excess body weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, increasing the risk of pain and injury.
3. Common Joint Issues: Understanding potential joint problems can help with early detection and management:
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joints, resulting in pain and swelling.
- Injuries: Sprains, strains, and fractures can occur due to trauma or overuse, affecting joint function.
In summary, understanding joint health involves recognizing the anatomy of joints, factors that influence their function, and common issues that can arise. By prioritizing joint care through a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and regular exercise, you can promote long-term joint health and mobility.

Key Nutrients for Joint Function
Key nutrients for joint function are essential for maintaining healthy joints and preventing discomfort. These nutrients support the structure of joints, reduce inflammation, and promote overall joint health. Here are some of the most important nutrients to consider:
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), walnuts, and flaxseeds, omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce joint pain and stiffness, making them a critical addition to the diet for anyone experiencing joint issues.
2. Glucosamine: A natural compound found in cartilage, glucosamine is often taken as a supplement to support joint health. It helps maintain cartilage structure and can alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis.
3. Chondroitin: Often paired with glucosamine, chondroitin is another component of cartilage that helps retain water and maintain its elasticity. It can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
4. Vitamin C: This antioxidant is crucial for collagen synthesis, which is necessary for maintaining the integrity of cartilage. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
5. Vitamin D: Essential for calcium absorption, vitamin D plays a vital role in maintaining bone health. Adequate vitamin D levels can help prevent joint pain and reduce the risk of developing arthritis. Sun exposure, fatty fish, and fortified foods are excellent sources of vitamin D.
6. Calcium: Essential for strong bones, calcium helps support joint function by ensuring the integrity of the skeletal system. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milks are good sources of calcium.
7. Antioxidants: Nutrients like vitamin E, selenium, and various phytonutrients found in fruits and vegetables help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, supporting overall joint health.
Incorporating these key nutrients into your diet can significantly enhance joint function and reduce the risk of joint-related issues. A balanced diet rich in these nutrients, combined with a healthy lifestyle, can promote long-term joint health and improve overall well-being.
How Nutrients Help Reduce Inflammation
How nutrients help reduce inflammation is a crucial aspect of maintaining joint health and overall wellness. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or stress, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including joint pain and degenerative diseases. Here’s how specific nutrients can play a role in reducing inflammation:
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They help inhibit the production of inflammatory substances in the body and can reduce joint pain and stiffness associated with conditions like arthritis. Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods can lead to significant improvements in inflammation levels.
2. Antioxidants: Nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium act as antioxidants that help fight oxidative stress in the body. By neutralizing free radicals, these antioxidants can help reduce inflammation and protect joint tissues from damage. Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries, nuts, and leafy greens, play a vital role in an anti-inflammatory diet.
3. Turmeric (Curcumin): While not a nutrient per se, curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is known for its powerful anti-inflammatory effects. It can inhibit various inflammatory pathways in the body and is often recommended as a supplement for joint health.
4. Vitamin D: Adequate levels of vitamin D are essential for regulating the immune system and reducing inflammation. Studies suggest that low vitamin D levels are associated with increased inflammation, making it important to ensure you get enough through sun exposure or fortified foods.
5. Magnesium: This mineral plays a role in hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body and is known to help regulate inflammatory responses. Magnesium-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and whole grains can promote lower inflammation levels.
6. Fiber: A diet high in fiber can aid in reducing inflammation. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, beans, and fruits, has been shown to lower inflammatory markers in the body.
By incorporating these nutrients into your diet, you can help manage and reduce inflammation, leading to better joint health and improved overall well-being. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet combined with a healthy lifestyle can significantly influence inflammation levels and support long-term health.

Food Sources of Nutrients for Joints
Food sources of nutrients for joints play a vital role in supporting joint health and reducing inflammation. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into your diet can help ensure that you receive the essential vitamins and minerals necessary for optimal joint function. Here are some key food sources for important nutrients:
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
– Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna.
– Plant-based sources like walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds.
2. Glucosamine and Chondroitin:
– These are not typically found in foods but can be sourced from supplements derived from shellfish or synthetic sources. Bone broth is also a good option, as it contains collagen and other compounds that support joint health.
3. Vitamin C:
– Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, lemons), strawberries, kiwi, bell peppers, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts are excellent sources of vitamin C.
4. Vitamin D:
– Fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), fish liver oils, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks are good sources. Sun exposure also helps the body synthesize vitamin D.
5. Calcium:
– Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), dark leafy greens (kale, collard greens), fortified plant-based milks, and almonds are rich in calcium.
6. Antioxidants:
– Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), nuts (especially walnuts and pecans), dark chocolate, and green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale) are abundant in antioxidants.
7. Magnesium:
– Foods rich in magnesium include nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds (pumpkin seeds), whole grains (quinoa, brown rice), and legumes (black beans, lentils).
8. Fiber:
– Fruits (apples, pears), vegetables (carrots, broccoli), whole grains (oats, barley), and legumes (beans, lentils) are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
Incorporating these food sources into your daily diet can significantly contribute to the health of your joints. A balanced approach that includes a variety of nutrients will not only support joint function but also promote overall health and well-being.
Supplements for Joint Health
Supplements for joint health can play a significant role in supporting and maintaining the function of joints, especially for individuals experiencing discomfort or those at risk of joint-related issues.
While it’s always best to obtain nutrients from food sources, supplements can help fill dietary gaps and provide concentrated doses of essential nutrients. Here are some commonly used supplements for joint health:
1. Glucosamine: Often derived from shellfish or manufactured synthetically, glucosamine is a popular supplement that may help maintain cartilage integrity and alleviate joint pain associated with osteoarthritis.
2. Chondroitin: Frequently paired with glucosamine, chondroitin is believed to help reduce pain and improve joint function by promoting the retention of water in cartilage and preventing its breakdown.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Available in fish oil or flaxseed oil supplements, omega-3s are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce joint pain and stiffness.
4. Turmeric (Curcumin): Turmeric supplements, which contain curcumin, are praised for their powerful anti-inflammatory effects. They can help alleviate joint pain and improve function, making them a popular choice for those with arthritis.
5. Collagen: Collagen supplements, often in hydrolyzed form, can support joint health by providing the necessary building blocks for cartilage repair and maintenance.
6. Vitamin D: For those with low vitamin D levels, supplementation can be beneficial for bone health and may help reduce the risk of joint pain and inflammation.
7. Boswellia Serrata: This herbal extract is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and has been used in traditional medicine to support joint health and alleviate pain.
8. MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane): MSM is a sulfur-containing compound that may help reduce pain and inflammation in joints, promoting overall joint function and comfort.
Before starting any new supplement regimen, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure that the supplements are suitable for your specific needs and health conditions.
Combining supplements with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle can optimize joint health and enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining joint health is essential for overall mobility and quality of life. Understanding the anatomy and function of joints, along with the key nutrients that support their health, can empower you to make informed dietary and lifestyle choices.
Nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, vitamins C and D, and antioxidants play vital roles in reducing inflammation and promoting joint functionality.
Incorporating these nutrients through a balanced diet rich in whole foods, as well as considering supplements when necessary, can significantly enhance joint health and reduce discomfort.
Regular physical activity, proper rest, and seeking professional advice when needed are also crucial components of a comprehensive joint health strategy.
By prioritizing joint care, you can enjoy an active lifestyle and maintain independence as you age. Remember, every individual’s needs are unique, so it is important to tailor your approach to support your specific joint health goals.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Joint Health
What nutrients are essential for joint health?
Key nutrients include omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, vitamin C, vitamin D, calcium, and antioxidants.
How do omega-3 fatty acids benefit joints?
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce joint pain and stiffness.
Are there specific foods that support joint health?
Yes, foods rich in omega-3s, vitamin C, and antioxidants, such as fatty fish, citrus fruits, and berries, support joint health.
When should I consider taking joint supplements?
Consider supplements if you have dietary gaps, experience joint pain, or need concentrated doses of specific nutrients.
What role does physical activity play in joint health?
Regular physical activity helps maintain flexibility, strength, and overall joint function, reducing the risk of stiffness and injury.
How can I manage joint pain effectively?
Managing joint pain can involve a combination of proper nutrition, regular exercise, physical therapy, and possibly supplements.